Imagine you’ve just delivered a project – on time and within budget. However, critical bugs emerge upon launch, features fall short of expectations, and clients express frustration. As a result, rework piles up, deadlines get pushed back, and team morale… goes down. This is why project quality management should be equally prioritized as project management (new to the industry? Check the video below to get started).
And there are no shortcuts except knowing the basics, its importance, and so on. In this blog, let’s tick one box at a time.
What Is Project Quality Management?
Project Quality Management (PQM) is the systematic process of ensuring that your project deliverables meet (and ideally exceed) stakeholder expectations.
It’s not about achieving perfection (which, let’s be honest, is often an elusive goal).
It’s rather about proactively defining what ‘quality’ means for your specific project, putting processes in place to achieve it, and continuously monitoring progress to ensure you stay on track.
But then…
Isn’t ‘quality’ a relative term?
Yes, that is true. Defining quality can have several perspectives – of the team’s, customers’, comparison with other projects, etc. So, what’s acceptable for one client may not work for another.
But what’s the need for quality management, anyway? Well, for that, you need to know about the three key pillars.
The 3 Pillars of Project Quality Management
The 3 pillars of quality management outline the project’s quality objectives, the procedures that will be used to achieve those, and how quality will be monitored throughout the project lifecycle.
Quality Planning
This is where you define what “quality” means for your project.
It involves setting clear and measurable quality goals, outlining quality standards, and identifying potential risks to quality. This involves several key steps, such as –
- Identifying stakeholder expectations for the project’s deliverables. This might include functional, performance, usability, and aesthetic requirements.
- Developing a quality management plan that includes details on quality control and assurance activities, roles and responsibilities, communication protocols, and documentation procedures.
- Defining clear and measurable criteria for how you will assess the quality of project deliverables. This might involve industry standards, best practices, or client-specific requirements.
- Brainstorming potential issues that could threaten project quality. This list can include scope creep, resource constraints, communication breakdowns, or technical challenges.
Read More: What Is Project Planning - Steps, Importance, Examples, & More
Quality Assurance
Here, you focus on preventing defects from occurring in the first place.
It involves systematic audits and process reviews to ensure the project meets the defined quality standards. The goal is to build confidence that the project will meet its quality objectives by consistently applying best practices.
So, what are these best practices? I’ll discuss some of them –
- Conduct Reviews: Regularly schedule peer reviews, code reviews, design reviews, etc., to identify roadblocks early in the development process.
- Perform Inspections: Conduct formal inspections of project artifacts, such as designs, code, and documentation, to ensure they meet quality standards.
- Implement Quality Gates: Establish checkpoints throughout the project lifecycle where progress is assessed against quality criteria before moving forward.
- Develop a Culture of Quality: Foster a team environment where quality is valued and everyone is encouraged to report potential problems.
Here’s a project quality management example –
A software development team might implement automated tests to ensure the code meets the project’s quality standards. They can ensure this by conducting regular code reviews to identify any issues.
Quality Control
This involves actively monitoring your project and identifying any deviations from your quality standards.
Monitoring and measuring the project’s outputs against the established quality standards is vital. Here, having a reliable project management system in place is a must-have for your team.
Let’s discuss some of the reasons why –
- Task Management: For definable outcomes, a task management tool allows you to define clear, actionable tasks that align with the project’s quality objectives.
- Shared Calendar: This can help you control quality, ensuring all team members know about quality-related tasks and deadlines.
- Reporting & Analytics: The reliability in project execution is supported by detailed reporting and analytics, which track quality consistency across tasks and deliverables.
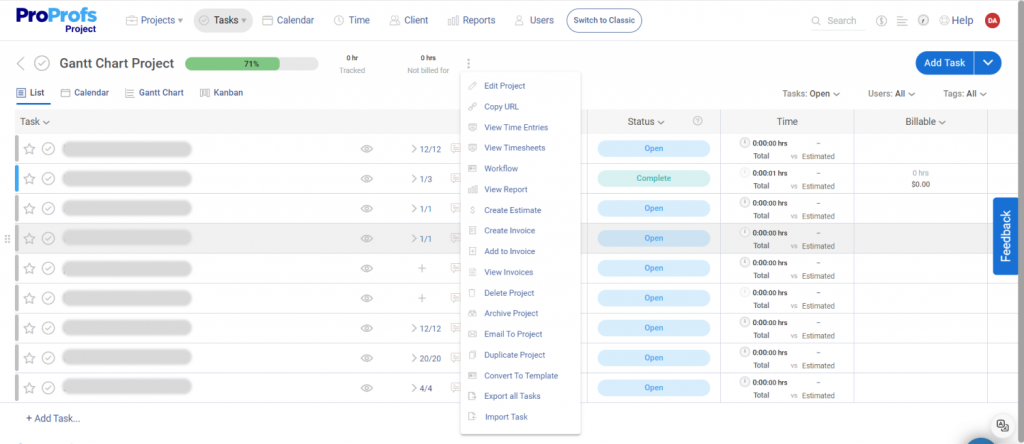
(Image source: ProProfs Project)
- Gantt Charts: You can use Gantt charts, a common tool in project management software, for project planning and monitoring.
Although this is the dedicated stage, where the project’s deliverables are inspected for defects and discrepancies, quality control should ideally be done at every other step as well. When issues are identified, corrective actions should be taken to prevent recurrence.
Why Is Project Quality Management Important?
Project quality management is about meeting specifications, delivering value, and ensuring that the project’s outcomes align with the business objectives and customer needs.
So, let’s talk about its importance below –
- Increased Customer Satisfaction: When you deliver high-quality projects that exceed expectations, you build trust, foster long-term relationships, and generate positive word-of-mouth referrals. This can lead to repeat business, increased customer lifetime value, and a stronger competitive advantage.
- Reduced Rework: You save time and resources by identifying and addressing issues early on. Without quality management, that would otherwise be wasted on fixing problems later in the development cycle.
- Improved Team Morale: Working on a project that consistently produces quality results motivates teams and fosters a sense of accomplishment.
- Enhanced Profitability: Reduced rework, increased client satisfaction, and improved project efficiency all contribute to a healthier bottom line.
- Mitigated Risk: Identifying and addressing potential quality issues early helps avoid project delays, cost overruns, and reputational damage.
What Are Some of the Best Tools for Project Quality Management?
Let’s look at the most popular project quality management tools that can help you assess the quality of your project and improve it when you still have time.
Gantt Charts
Gantt charts can be considered a valuable tool in project quality management.
Gantt charts are primarily used for scheduling and tracking project timelines.
However, the fact that it provides a visual representation of the project schedule – showing when each activity should start and finish, how long it will take, and where activities overlap with one another – helps project managers ensure that tasks are completed on time and that the project stays on track.
Affinity Diagrams:
Affinity Diagrams are used to organize a large number of ideas into logical groups. This tool is particularly useful during brainstorming sessions when the project team needs to sift through complex information and categorize it in a way that facilitates understanding and action.
(Image created using DALL-E)
Process Decision Program Chart (PDPC):
The PDPC is a tool that helps you anticipate potential problems and plan countermeasures. By identifying what could go wrong in a plan, you can develop strategies to mitigate risks and ensure that quality objectives are met.
(Image created using DALL-E)\
Interrelationship Diagrams:
These diagrams identify and analyze the cause-and-effect relationships among various project components. Understanding these interrelationships is crucial for determining the root causes of quality issues and addressing them effectively.

(Image created using DALL-E)
Prioritization Matrices:
Prioritization Matrices enable project teams to focus on the most critical quality issues. Teams can allocate resources more efficiently by evaluating and ranking problems based on their severity and potential impact.
The “Eisenhower Matrix” is a great example of a prioritization matrix –
(Image Source: LinkedIn)
Network Diagrams:
Network Diagrams are visual representations of a project’s activities and their dependencies. They are instrumental in planning and scheduling project work, ensuring that quality tasks are integrated into the project timeline.

(Image created using DALL-E)
Matrix Diagrams:
Matrix Diagrams are used to display the relationship between different sets of data. They can help compare and contrast factors affecting quality, such as the alignment between project objectives and quality standards.
Here are some of the different types of Matrix Diagrams –
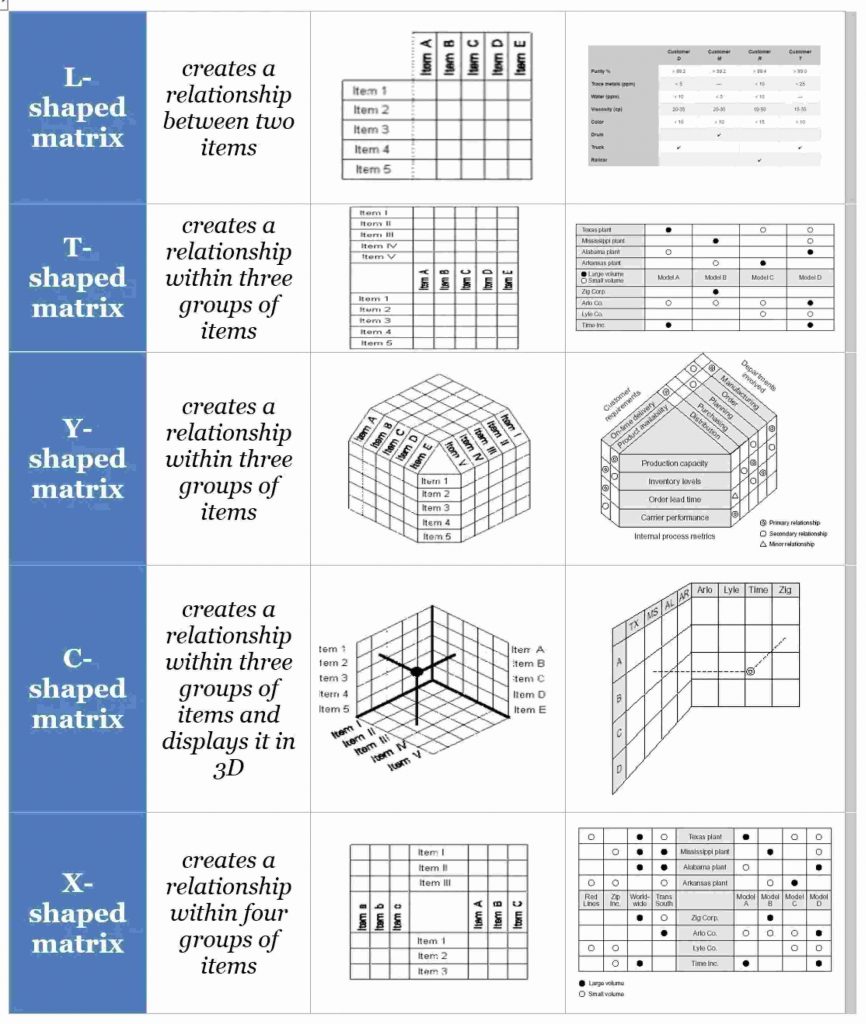
(Image source: Project Management Academy)
Read More: Project Time Management: Process & Strategies to Improve Time Management
Steer Your Way to Project Excellence With ProProfs Project
Project quality management is an ongoing journey, not a one-time destination. By implementing the principles and tools discussed here, you’ll ensure projects meet deadlines and client expectations.
Also, I believe using a project management software system is important in that journey. Why? That’s because overseeing project quality is a big job.
You must constantly check on establishing quality objectives for your team to achieve, determine the methods for assessing these objectives, and document the outcomes. A platform such as ProProfs Project makes things easy.
After all, why not when you can use Gantt charts for planning and monitoring tasks, manage them with a task management system, and use reports to see outcomes? It’s hard to describe the convenience unless you try it yourself. The good thing is a lot of project management software, like ProProfs Project, offers a freemium plan or a free trial. Try it today. It’s free!
FREE. All Features. FOREVER!
Try our Forever FREE account with all premium features!





