How do you decide whether an upcoming project will be profitable for the business? How do you determine whether investing resources, time, and effort in the venture will be fruitful?
Answering these questions requires you to have a solid understanding of project profitability.
This will help you make accurate bids in the future, optimize billable utilization, and make the right long-term investment decisions.
In this blog, I’ll explain the nitty-gritty of project profitability and highlight the strategies to improve it.
And if you’re new to project management, then this quick video will be helpful –
What Is Project Profitability?
Project profitability refers to the financial gain a project yields over its lifespan. It’s a straightforward concept: a project is profitable if it generates more revenue than the costs incurred to complete it.
Simply put, it’s the difference between the total revenue generated and the total costs incurred during the project lifecycle.
Think of it as the answer to this crucial question: Did this project make us money?
A high project profitability translates to a greater return on investment (ROI) and a more sustainable business model.
What Are the 3 Primary Measures of Project Profitability?
For project profitability analysis, you should rely on three key metrics that cut through the noise and give you a clear picture of your project’s financial health.
Here’s a breakdown of what they mean and why they matter –
Net Profit Margin
Imagine this as a percentage grade on your project’s money-making ability. It shows what slice of your total revenue remains after you’ve covered all the project expenses.
A higher Net Profit Margin is good news, indicating your project is efficient at turning revenue into actual profit. Net Profit Margin is calculated by dividing the net profit by the total revenue and multiplying by 100 to get a percentage:
Here’s an example to help you understand it better:
Imagine the total revenue agreed upon in the contract of completing a construction project is $1,000,000. Throughout the project, the company incurs various costs, such as –
- Direct materials (such as cement, steel, glass): $300,000
- Labor (wages for workers): $250,000
- Equipment (rentals for machinery): $100,000
- Indirect costs (office expenses, utilities, legal fees): $150,000The total expenses for the project thus sum up to $800,000. To find the Net Profit Margin, you subtract the total expenses from the total revenue and then divide by the total revenue:
- Net Profit = Total Revenue – Total Expenses = $1,000,000 – $800,000 = $200,000
- Net Profit Margin = (Net Profit / Total Revenue) x 100 = ($200,000 / $1,000,000) x 100 = 20%
In this example, the Net Profit Margin is 20%, which means that for every dollar earned from the project, the company keeps $0.20 as profit after covering all its expenses.
This margin indicates the financial efficiency of the project, showing how well the company manages its costs relative to the revenue generated.
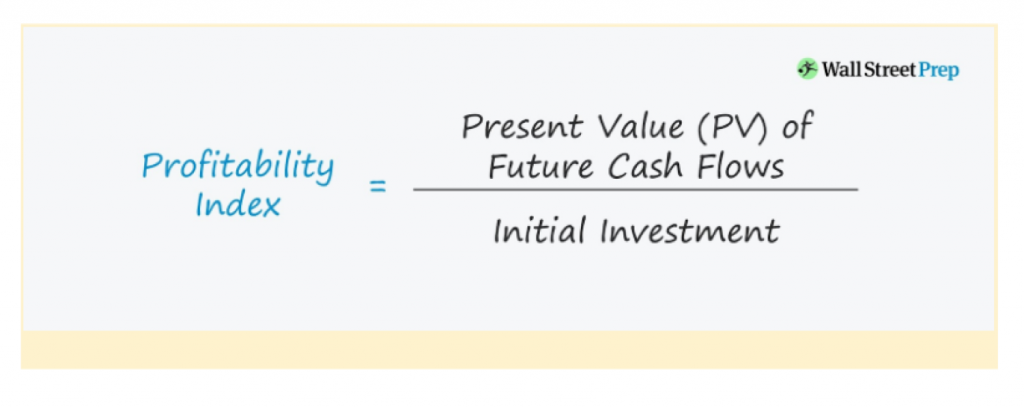
Profitability Index (PI)
This metric goes beyond a simple profit number, considering the time value of money.
It calculates the total value of all the cash flow your project will generate in the future, compared to the initial investment you made upfront. Simply put, PI tells you how much money you get back for every dollar you invest.
Let’s once use our project profitability calculator and check an example to see how it works:
Suppose a company plans to invest in a new product line and estimates the initial investment for equipment, research, and development will be $500,000. The expected cash flows over the next five years from selling this product are projected as follows:
- Year 1: $100,000
- Year 2: $120,000
- Year 3: $150,000
- Year 4: $180,000
- Year 5: $200,000
To calculate the PI, we first need to determine the present value (PV) of the future cash flows. Assuming a discount rate of 10%, the present values for each year are:
- Year 1: $100,000 / (1 + 0.10)^1 = $90,909
- Year 2: $120,000 / (1 + 0.10)^2 = $99,174
- Year 3: $150,000 / (1 + 0.10)^3 = $112,697
- Year 4: $180,000 / (1 + 0.10)^4 = $123,967
- Year 5: $200,000 / (1 + 0.10)^5 = $124,183
The total present value of the future cash flows is:
$90,909 + $99,174 + $112,697 + $123,967 + $124,183 = $550,930
Now, we calculate the Profitability Index:
PI = Total PV of Future Cash Flows / Initial Investment = $550,930 / $500,000 = 1.10
A PI of 1.10 indicates that the company expects to create a value of $1.10 for every dollar invested in the project. Since the PI is greater than 1, this project is considered financially viable and suggests a good return on investment.
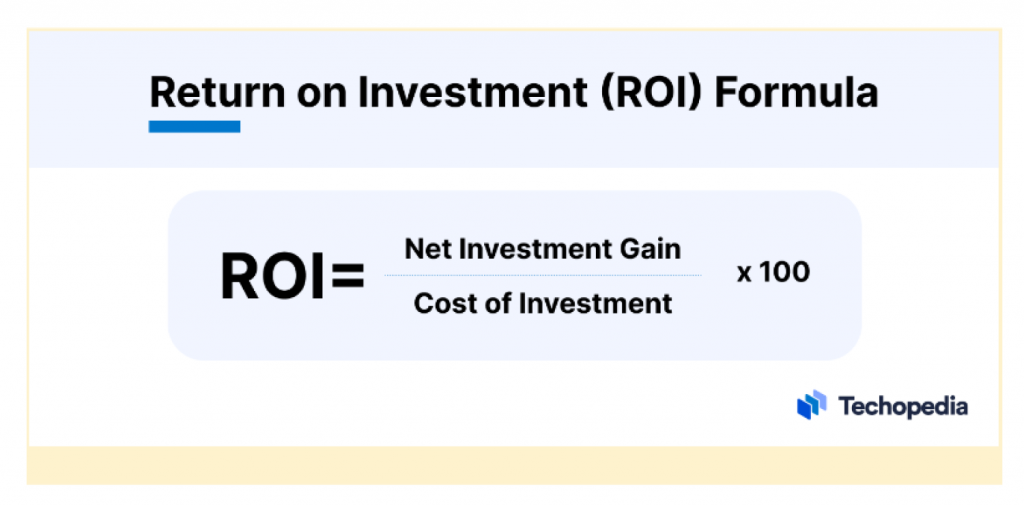
Return on Investment (ROI)
ROI measures the gain or loss generated on an investment relative to the money invested. It is expressed as a percentage and is used to compare the efficiency of different investments.
In the context of project management, a high ROI means the project is generating significant returns relative to its costs. Here’s how you can calculate ROI –
Here’s a theoretical example to help you understand ROI better –
Consider a consulting firm that invests $200,000 in developing a new software application to streamline internal processes.
They estimate the application will save them $100,000 annually in operational costs over five years. Here’s how ROI helps assess the value of this investment:
- ROI = (Net Profit) / (Initial Investment) x 100
- Net Profit, in this case, is the total cost savings over the project lifespan: ($100,000/year) x 5 years = $500,000
- ROI = ($500,000) / ($200,000) x 100
- ROI = 250%
In this scenario, the ROI is 250%. This indicates that for every dollar invested in developing the software, the firm will see a net profit of $2.50 over the five-year period.
How Do You Improve Project Profitability?
To achieve profitability, you must adopt some of the best practices that enhance team efficiency while keeping track of the key metrics to be achieved.
Let’s walk you through the steps to increase project profitability for your business.
Step 1: Plan It Out
Develop a detailed project plan outlining SMART goals, specific deliverables, and a breakdown of the resources needed (people, equipment, software). This roadmap keeps everyone aligned and helps identify potential problems early on, avoiding costly surprises later.
Those using a project management platform will likely benefit from the built-in templates to streamline the planning process and assign tasks with clear deadlines.
You can also visually map the project workflow with tools like Gantt charts.
Step 2: Improve Project Scope Management
Clearly define the project’s boundaries (scope) at the outset with a signed Scope of Work document from all stakeholders. Use a structured change management process to handle any necessary project scope adjustments efficiently.
To improve scope management, conduct regular project reviews to identify and reject any new feature requests that fall outside the original scope.
You can utilize project management tools with features like task baselines to track deviations from the original plan and identify scope creep early on. Version control features ensure everyone can easily track project changes and stay updated.
Read more: Project Scope: How to Define & Manage It Like a Pro
Step 3: Optimize Resource Allocation
When you don’t have the right team with the appropriate skills for each task, you’re likely to see roadblocks and, eventually, a project dealing with losses. So, efficient resource management is a vital step when improving project profitability.
For this, you’ll need a resource planning tool. There, you can visualize team member workloads and identify who has free bandwidth and who is overloaded.
You can also use skills matrices to assess team member capabilities and identify knowledge gaps. Sometimes, team managers consider cross-training team members to increase overall project flexibility.
Suggested read: 15 Best Resource Management Software & Tools Of 2024
Step 4: Create Realistic Cost Estimates
Leverage past project data and industry benchmarks to create realistic cost estimates. A Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) can break the project into smaller, more manageable tasks.
Here’s a brief overview of what you need to do –
- Estimate the required time, labor, and other material or software costs for each task.
- Factor in potential risks like unexpected delays or resource availability issues.
- Allocate contingency funds (typically 10-15% of the total budget) to handle unexpected expenses.
- Keep a buffer to prevent budget overruns that can sink your profitability.
Personally, I prefer using built-in cost estimation solutions, which are available on some project management platforms.
They factor in historical data and industry benchmarks to track actual costs against your estimates throughout the project lifecycle – allowing for real-time adjustments if needed.
Related post: What Is Cost Management in Project Management?
Step 5: Maintain Open Communication
Having open communication channels with clients to discuss project costs and potential budget adjustments helps establish transparency among all stakeholders.
Conduct regular client meetings to discuss project progress and highlight potential cost variances. Be upfront and proactive in proposing solutions (like value engineering or alternative materials) if budget adjustments become necessary.
Now, all these may become messy if you’re managing projects in the traditional doc-and-spreadsheet way. But with a project management system, it’s different. That’s because you can –
- Set up a team to manage projects and tasks
- Add followers to each task for effective supervision
- Invite clients as guests to your project, and let them keep track of changes
- Share real-time project data and reports with clients
People also read: 10 Best Project Collaboration Software of 2024
Step 6: Plan for the Unexpected (Risk Management)
Even after careful project management planning, risks can threaten profitability. That’s why proactively identifying and mitigating potential project risks is necessary.
So, what are you supposed to do about it?
First, risk assessments should be conducted early in the project lifecycle to brainstorm potential issues and their likelihood. Based on the results, develop contingency plans to address these risks, outlining mitigation strategies and alternative solutions.
I’ve also seen many project managers using a project management platform to identify, assess, and prioritize risks.
Read More: How to Overcome Risks Using a Comprehensive Risk Management Plan
What Are the Elements of Project Profitability?
The elements of project profitability are the fundamental building blocks that influence how much financial gain a project generates. Let’s look closely at them to understand how they make an impact –
1. Resources:
This encompasses everything you need to execute the project and turn ideas into reality. Usually, resources consist of –
- People: This includes your team members’ salaries, benefits, and training costs. Optimizing their skills and utilization is crucial for controlling project expenses.
- Equipment: This covers any specialized equipment required for the project, including rental or purchase costs, maintenance fees, and associated consumables.
- Hardware/Software: Factor in licensing fees for software needed for the project, hardware purchases (e.g., computers), and ongoing maintenance costs.
2. Time:
Effective time management directly impacts project profitability. Here’s why –
- Task Durations: Accurately estimating the time required to complete each project task is essential. Delays can lead to cost overruns. Here, you can use a project management software solution with time-tracking capabilities.
- Schedule Management: Creating a realistic project schedule and actively monitoring progress helps ensure tasks are completed on time and within budget.
- Time Value of Money: Generally, sooner is better. Completing a project early allows you to collect revenue faster and capitalize on the time value of money.
3. Money:
Needless to say, this is the financial lifeblood of your project. Here’s what you should consider:
- Budget: Develop a comprehensive project budgeting that outlines all anticipated costs associated with resources, materials, labor, and any potential contingencies.
- Cost Tracking: Carefully track all project expenses throughout the project lifecycle. Identify variances between the budget and actual costs to understand where adjustments might be needed.
- Contingency Funds: Allocate a buffer in your budget to address unforeseen expenses or unexpected risks that could arise during the project.
4. Scope:
A clearly defined project scope keeps everyone on the same page and prevents uncontrolled project creep. Here’s why scope matters –
- Project Deliverables: Clearly define the specific outputs or outcomes the project will deliver.
- Project Goals: Establish clear and measurable goals for the project. Ensure these goals are aligned with the overall business objectives and contribute to the project’s value proposition.
- Scope Management: Proactively manage project scope throughout the project lifecycle. Communicate effectively with stakeholders and avoid scope creep by carefully evaluating and rejecting any requests for additional features that fall outside the original plan.
Drive Projects to Maximum Profitability With ProProfs Project
Every company wants to make profits. However, hardly a few understand how to conduct profitability analysis in project management. You see, it’s not a complicated process as long as you know the systematic steps, the elements, and the other whereabouts as discussed in this blog.
Software like ProProfs Project helps streamline project profitability by tracking key metrics, analyzing resource costs, prioritizing profitable projects, optimizing resource utilization, and monitoring budgets.
Sign up for free today to start driving projects to maximum profitability!
Learn More About Project Profitability
What are the 5 main phases of a project?
The five main phases of a project life cycle are –
- Initiation: Defining project goals, scope, and feasibility.
- Planning: Creating a detailed project plan with timelines, resources, and budget.
- Execution: Carrying out the project tasks according to the plan.
- Monitoring & Controlling: Tracking progress, identifying deviations, and making adjustments as needed.
- Closure: Finalizing deliverables, evaluating project success, and documenting lessons learned.
What is the project lifecycle?
The project lifecycle is a structured framework that outlines the different stages a project goes through, from its initial conception to final completion. It typically involves five phases: initiation, planning, execution, monitoring & control, and closure. Each phase has specific goals and deliverables, moving the project toward completion.
What is project profit and loss?
Project profit and loss (P&L) is like a scorecard for your project’s finances. It shows if it made money (profit) or lost money (loss) by comparing the total income (revenue) from the project to all the expenses spent throughout its lifecycle.
FREE. All Features. FOREVER!
Try our Forever FREE account with all premium features!