Ever stuck in the never-ending loop of sudden ‘urgent tasks’ that hamper project progression? Or do you often face resource limitations while in the middle of a project?
You see, it’s not easy being a project manager.
You need to keep track of numerous things, especially in the modern-day business environment that constantly aims to exceed targets and multiply profits. And yes, all that comes at a cost—conveniently ignoring overburdening tasks and a mismanaged project workflow.
However, all this can change when you understand the various phases and techniques of a project management process. That’s exactly what we are about to discuss in this blog. Meanwhile, if you’re new to project management, don’t forget to get a quick heads-up by watching this video –
What Is the Project Management Process?
Project management process is a systematic series of activities that every project has to go through. It is commonly termed as the “project management lifecycle,” and consists of 5 distinct phases –
- Initiation
- Planning
- Executing
- Monitoring & Controlling
- Closing
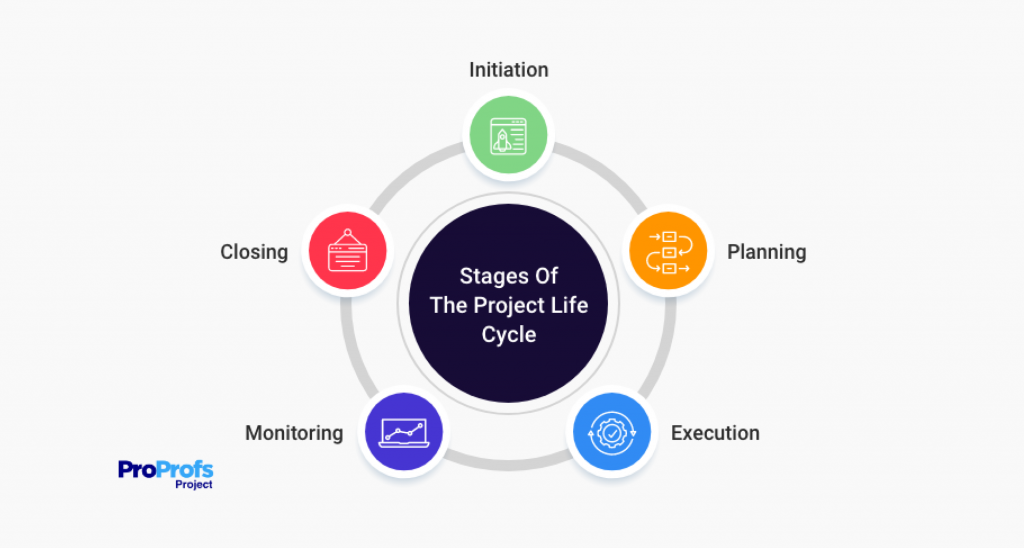
These processes ensure that a project progresses from initiation to completion in a controlled and orderly manner. Let’s now take a look at each phase in more detail.
What Are the 5 Major Project Management Processes?
Project managers need to remember that all these phases are important for the project’s success. So, it’s important to clearly understand what to do in each phase and how project management software can help with that.
1. Initiation
The initiation stage marks the beginning of project management, where the project’s value, advantages, and practicality are evaluated. The primary instruments for this stage are the business case document and the benefits management plan.
So, what are they?
- The business case outlines the overarching concept and justification for the project’s necessity.
- On the other hand, the benefits management plan outlines the methods and timing for realizing the project’s advantages.
Should the project be deemed feasible, a new document, the project charter, is drafted. It acts as a green light for the project, granting permission to allocate company resources. This is also where you need to identify key stakeholders.
Want to learn more about the ‘initiation’ phase? Read this blog –
Project Initiation: What Is the Right Way to Start a Project in 2024?
2. Planning
I’ve heard a lot of project managers say that this is the most vital part of the project lifecycle. And there are obvious reasons for that.
Project planning is the phase where project teams huddle up to chart the project’s course. This is where project managers roll up their sleeves and get down to business, tackling the bulk of their tasks.
This phase involves creating detailed work breakdown structures (WBS) – essentially, breaking down the project into manageable tasks.
Here’s an example of how a WBS may look for a construction project –
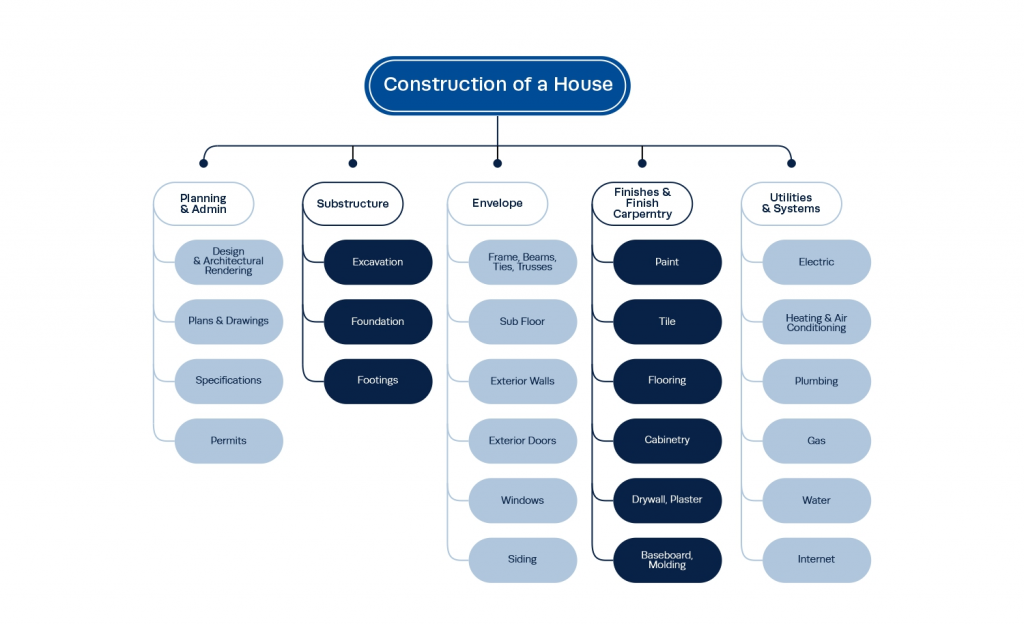
(Image source: Institute of Project Management)
In the planning phase, you must also define scope, schedule, cost, quality, resources, risk, you name it—into a cohesive plan. It includes setting up a strategy for all stakeholders.
Now, some of you may ask – what’s the endgame of project planning?
Well, it is to create a clear, actionable roadmap complete with goals and milestones that everyone can reach. And these must be –
- SMART – Specific, measurable, attainable, realistic, timely, and
- CLEAR – Collaborative, limited, emotional, appreciable, refinable
At this point, if you’re wondering whether you should invest in a trusted project management system, I’d recommend a ‘Yes.’ And here are some reasons why –
- Defining Project Scope: Helps you clearly outline the project’s boundaries, including objectives, deliverables, and requirements.
- Scheduling: Enables the creation of detailed timelines, including start and end dates for project tasks, ensuring that milestones are met on time.
- Risk Management: Helps identify potential risks and develop mitigation strategies to prevent project delays and scope creep.
- Budgeting: Aids in estimating the project budget, accounting for all costs associated with resources, materials, and contingencies.
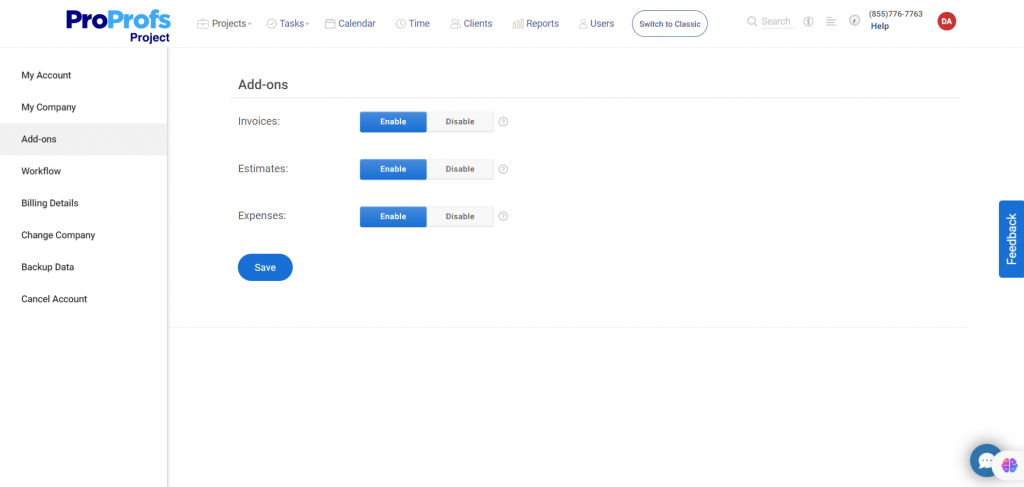
❗Did you know? Some project management software like ProProfs Project even lets you automate invoices, estimates, and expenses with add-ons.
Read more about project planning –
What Is Project Planning – Steps, Importance, Examples, & More
3. Execution
Drawing from the blueprint in the planning phase, your project team gets down to business, turning plans and documents into reality.
As a project manager, you need to be on the front line, ensuring that the project’s resources are working as per the plan. And it’s not just about ticking off tasks. It is rather about ensuring that the team learns how everything works for future projects.
The project execution phase is also one of the most pivotal project management process steps where quality management is taken care of.
Project managers must be vigilant to ensure everything is up to snuff and meets the high standards set out from the start. Feedback and strategies should be exchanged to boost the team’s game.
Before moving to the next phase, let’s quickly discuss what benefits you get by using a project management platform –
- Task Management: With a task management tool, you can assign tasks, set deadlines, and track progress in real time.
- Quality Assurance: Project management platforms allow continuous quality checks by integrating feedback loops into task completion, ensuring deliverables meet the set standards.
- Team Collaboration: It’s always good to have built-in team collaboration features to easily set up teams, share files, tag others, etc. – keeping everyone in sync.
- Resource Allocation: Some project management platforms have a resource planning tool, allowing you to allocate manpower and materials where needed most.
(Image source: ProProfs Project)
4. Monitoring & Controlling
Although it’s a different phase of the project management process, it runs side-by-side with project execution.
As the name suggests, this phase is all about measuring project performance and progression in accordance with the project plan. Here, project managers use key performance indicators (KPIs) and regular status updates to ensure the project’s direction aligns with the plan.
One of the best ways to monitor projects in real time is using Gantt charts. There, you can track the entire timeline, dependencies, and much more.
Also, with reporting features and dashboards, you can effortlessly manage changes and stay within budget and schedule. In my experience, that also goes a long way in risk management.
(Image source: ProProfs Project)
Read more: How to Track Your Project’s Progress
5. Closing
In the final phase of the project lifecycle, you (project managers) should wrap up all project activities, finalize deliverables, obtain necessary approvals, and formally close the project.
Here’s what you’re usually supposed to tick off the list:
- Getting the final sign-off from the customer
- Finalizing and closing project accounts
- Communicating about project closure to stakeholders
- Releasing the resource to the shared pool or other projects
- Track issues (if any) faced during or after the project met with its deadline
But that’s not all. Some companies also prefer a final team huddle – the project closure meeting. It’s where the team and stakeholders gather to swap stories from the trenches.
Here, using a project management platform, you can export a summary, profitability, timeline, and other reports in CSV format to share with stakeholders or preserve them for future reference.
For more information, read – Project Closure Steps and Checklist: The Ultimate Guide
What Are the Most Common Project Management Methodologies?
Project management is a field rich with methodologies, each offering unique advantages that cater to different project needs. In this section, I’ll help you explore the most common ones that are usually used.
- Waterfall:
The Waterfall model has a traditional and linear approach. It follows a sequential order: requirements, analysis, design, implementation, testing, deployment, and maintenance.
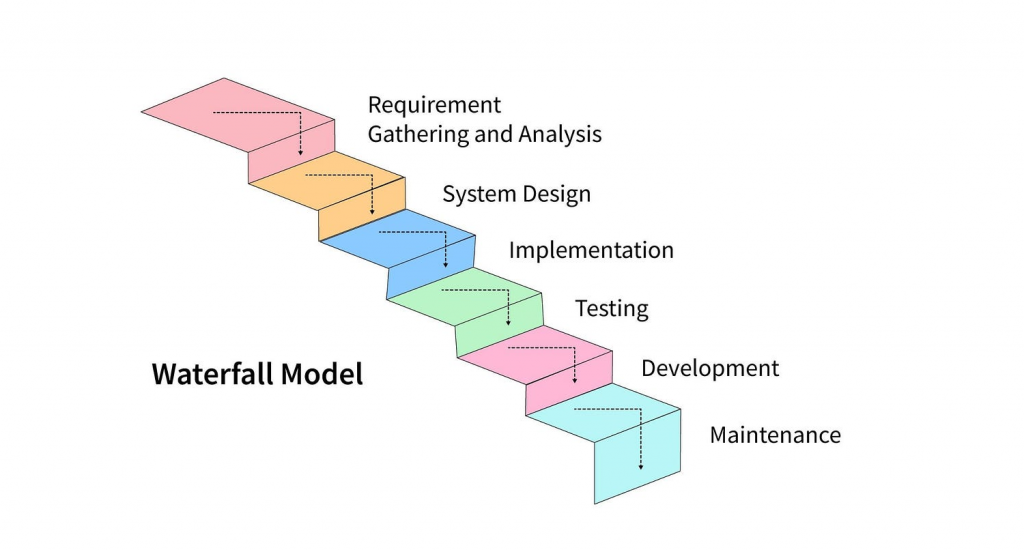
(Image source: Medium)
Each phase must be completed before moving to the next, making it suitable for well-defined projects with clear requirements upfront. Waterfall is often favored in construction, manufacturing, and legal industries due to its structured nature.
- Advantages: Streamlined workflow, clear phase gates, minimal rework (if requirements are well-defined)
- Disadvantages: Lacks flexibility, limited stakeholder involvement during later stages, can be time-consuming for complex projects
Learn more: A Guide to Waterfall Project Management Methodology
- Agile:
Agile project management is synonymous with flexibility and adaptability. It’s a technique that thrives on iterative development, where requirements and solutions evolve through continuous feedback and adaptation.
Here, projects are broken down into smaller chunks (sprints), allowing for adjustments based on learnings throughout the development cycle. It’s particularly beneficial in environments where project scopes are not fixed and change is expected.
Check out the graphical representation to have a better understanding:
(Image source: Medium)
- Advantages: Adaptable to changing requirements, increased stakeholder involvement, faster time-to-market
- Disadvantages: Requires a high level of team collaboration and communication, may not be suitable for projects with strict deadlines or fixed budgets
Related read: Top 11 Agile Project Management Software in 2024
- Scrum:
Scrum is a subset of Agile, designed to improve team productivity and deliver value quickly. It’s centered around a simple framework that encourages teams to work collaboratively and tackle complex problems.
Scrum is often visualized through boards and charts that track progress, making it a transparent method that promotes accountability and continuous improvement.
Here are some of the core principles of the Scrum methodology –
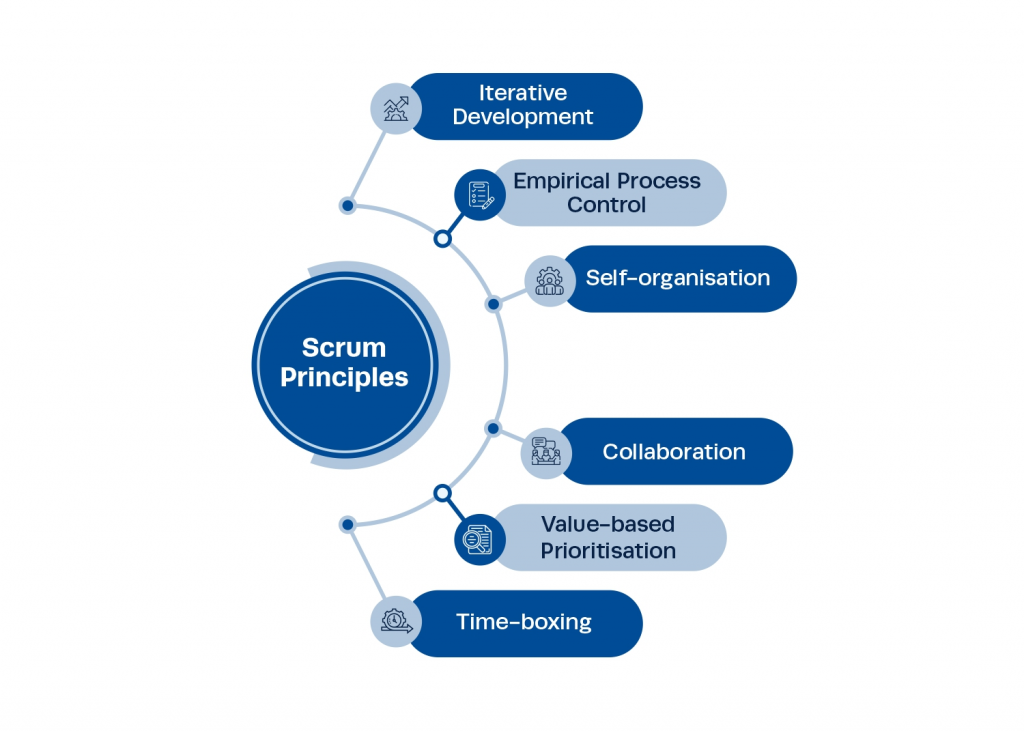
(Image source: Institute of Project Management)
- Advantages: Well-suited for projects with evolving requirements, short sprint cycles allow for continuous feedback and course correction
- Disadvantages: Can be challenging to predict exact delivery dates upfront, requires high levels of team communication and self-organization
Suggested post: Best Scrum Tools for Effective Project Management
- Kanban:
A visual project management technique that utilizes Kanban boards to track tasks. Tasks progress through different stages (e.g., To Do, In Progress, Done) and are visualized on the board.
If you’re new to the term “Kanban Boards,” check this video to have a quick overview –
The Kanban methodology is known for its focus on continuous flow and work-in-progress (WIP) limits to optimize efficiency. It enables you to see bottlenecks and optimize workflow for better efficiency.
Let’s quickly discuss the pros and cons of the methodology –
- Advantages: Highly adaptable to changing priorities, provides a clear visual representation of the project workflow
- Disadvantages: May not be ideal for highly complex projects with intricate dependencies between tasks
For a more detailed idea, read – Kanban Project Management: Everything you Need to Know
What Are the Benefits of Following a Structured Project Management Process?
I connected with some of the project managers I knew and asked them – how big a difference they felt before and after following a structured project management process.
And these are some benefits that they experienced first-hand with a robust process and software in hand –
- Improved Communication & Collaboration: Fosters a culture of transparency by providing a central platform for communication, task updates, and file sharing.
- Increased Project Success Rates: A well-defined roadmap, clear task allocation, and efficient resource management increase the chance of project completion within budget and timeframe.
- Enhanced Risk Management: Regular monitoring through project management software enables timely mitigation strategies, minimizing the impact of unforeseen challenges.
- Efficient Use of Resources & Time: Facilitates efficient resource allocation by visualizing project workloads. Additionally, task tracking and progress reports ensure time is spent productively on essential tasks.
- Clearer Project Visibility: Displays real-time project health and progress reports, giving you complete control over your project’s trajectory.
Drive Projects to Success With ProProfs Project
Being a project manager means overseeing everything. You need to check whether the project goes through the well-defined project management process in the right direction. But apart from that, it’s also essential that you invest in a good project management software system for your team.
Is it because it helps in the project management process improvement? Not really. Instead, it provides a platform where your team can stick to the five phases and follow a proven path toward sure-shot project success.
Say, for example, ProProfs Project is one of those software solutions that cater to startups and SMBs.
With an easy-to-understand interface, it comes loaded with advanced features like resource planning, portfolio management, project progress tracking views (Gantt charts, Kanban boards, etc.), task management, time tracking, reports, etc.
Plus, it has a freemium plan, which is absolutely great for small teams and first-time users. Try it today to start delivering quality projects within the set time frame.
Learn More About Project Management Process
How can I define project scope effectively?
Defining project scope effectively involves outlining what’s included (deliverables, tasks) and excluded from your project. Here’s a quick guide:
- Start with Goals: Identify your project’s objectives and desired outcomes.
- Define Deliverables: Outline the tangible outputs of your project.
- List Key Tasks: Break down the work required to achieve your deliverables.
- Set Clear Boundaries: Specify what’s NOT included in the project scope.
- Consider Constraints: Identify limitations like budget, time, and resources.
What are some common project management mistakes?
Here are some common project management mistakes to avoid:
- Unclear Scope: Vague goals and deliverables lead to confusion and scope creep.
- Poor Planning: Unrealistic timelines, resource misallocation, and lack of risk planning spell trouble.
- Communication Silos: Information gaps between team members and stakeholders cause delays and frustration.
- Avoiding Software: Not using a project management platform can hinder productivity and project success rates.
- Unrealistic Timelines: Underestimating the time needed for tasks sets your project up for failure.
- Ignoring Progress Tracking: Neglecting to monitor progress and identify deviations from the plan sets you up for failure.
FREE. All Features. FOREVER!
Try our Forever FREE account with all premium features!