“Give me six hours to chop down a tree, and I will spend the first four sharpening the axe.” – Abraham Lincoln.
Considering that your project is to ‘chop down a tree,’ this is how your ideal approach should be for Elements of Project Management. It emphasizes how the planning phase of ‘sharpening the axe’ requires brainstorming – without which even ‘six hours’ may feel less to cut down a tree.
Now, I know you’ll probably ask next – So, what’s a good project plan?
To answer that, you’ll need to learn about the most essential elements of Project Management or, to be more specific — the key components of project planning.
Now, before you move ahead, here’s a small video for those who are new to project management. Keep reading if you’re already a pro.
What Is Project Planning?
Project planning is the foundation on which successful projects are built. It’s the process of defining a clear roadmap, outlining the “what,” “when,” “who,” and “how” of achieving your project goals. It’s the act of defining your project’s objectives, scope, and the steps necessary to achieve them.
And if you talk about the project lifecycle, then ‘project planning’ is the second stage.
Read More: Must-Have Project Management Software Features Explained
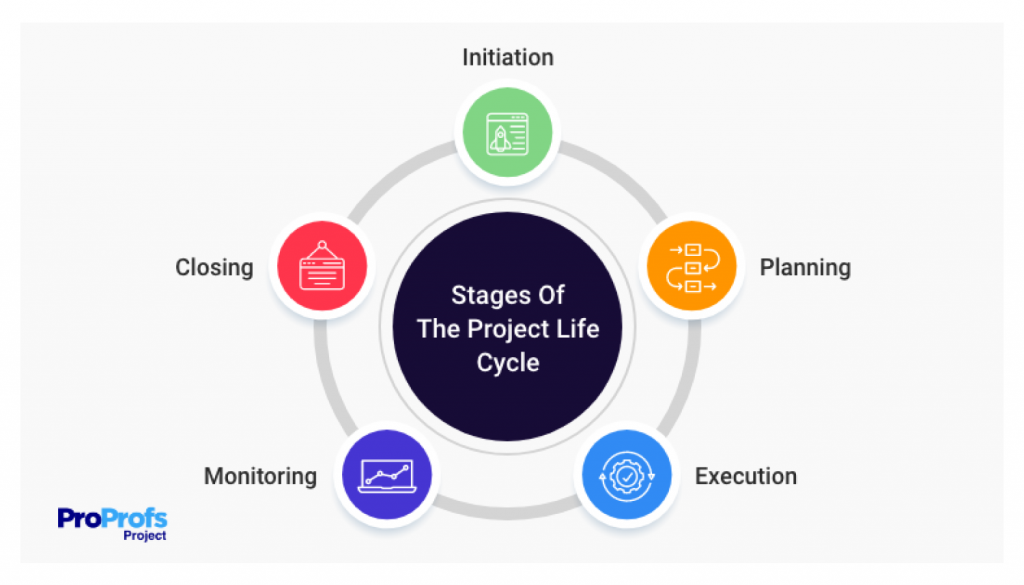
Read More: A Guide on Project Planning: The Steps, Benefits, Examples, & More
9 Key Elements of Project Management [Explained]
While the elements of project planning can vary depending on the project’s nature, some cover general aspects that are standard for all projects. Apart from business expectations, these key components usually include ways of overcoming unpredicted situations and beyond that.
So, what are they?
1. Scope
This is your project’s DNA – a crystal-clear understanding of what’s included (and excluded). It’s more like the boundary of the project. It outlines what will be delivered, detailing the tasks, deliverables, and boundaries.
Defining the scope involves understanding the project’s objectives and breaking them down into manageable tasks.
You can utilize methods like the Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) to do that and make it easier to control the scope.
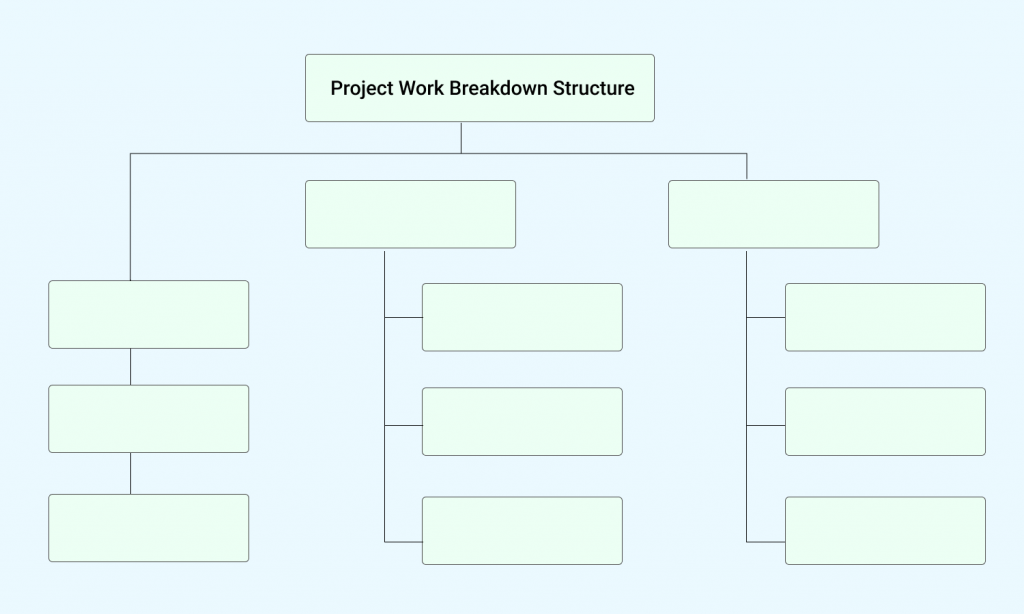
A well-managed scope is crucial to avoid scope creep that can inflate costs and deadlines.
2. Time
A project timeline is a schedule of activities, milestones, and deliverables. It’s a visual representation, often in the form of a Gantt chart, that helps everyone understand the sequence of tasks and their dependencies.
Developing a timeline requires estimating the duration of tasks, sequencing them, and allocating resources. It includes several steps, including –
- Identifying tasks & dependencies: List all the tasks involved in the project and identify any dependencies between them.
- Estimate task durations: For each task, estimate how long it will take to complete, considering its complexity, the skills of the assigned resource, and potential risks.
- Sequencing & scheduling: Use your task list and dependencies to determine the order in which tasks need to be completed. There might be some flexibility, so consider factors like resource availability and task criticality when creating your schedule.
Read More: How to Build a Project Timeline in 6 Simple Steps
3. Budget
This involves predicting the costs associated with the project. It’s not just about the initial estimates but about managing costs throughout the project lifecycle.
Estimate project costs meticulously, including labor, materials, and potential contingencies. Track expenses throughout the project to identify deviations and ensure you stay within budget.
One of the most common ways to manage budgets is to maintain a spreadsheet. But, in my experience, that often becomes a tedious task for complex projects.
There, I’d suggest you use a project management tool. Such a tool usually comes with different options like templates for creating budget tables, billing and invoices automation, etc.
4. Resource
Your project is only as strong as its team. And the team is only as strong as the available resources are.
Resource allocation involves assigning the most suitable resources to the right tasks at the right time. It involves balancing the availability of team members, equipment, and materials with the project’s needs, ensuring that resources are used efficiently. Proper resource management also ensures everyone’s workload is balanced.
(Image source: ProProfs Project)
Here are some of the best tips to manage resources like a pro –
- Prioritize tasks and allocate resources based on project criticalities to ensure high-impact areas are well-resourced.
- Use a resource planning tool to avoid overallocation and ensure balanced workload distribution.
- Regularly assess team capacity and skills to align resource allocation with project demands.
- Foster a culture of flexibility and cross-training to maximize resource adaptability and efficiency.
Read More: Project Resource Management 101: For Flawless Project Journeys
5. Procurement Management
As the name suggests, procurement management is the process of acquiring goods and services from external sources.
For a manufacturing project, procurement management would include negotiating with suppliers for raw materials, ensuring timely delivery, and managing contracts to ensure compliance with project timelines and budgets.
This is where you define-
- What products and services do we need?
- How and when do we need them?
- Who can be the best supplier?
- How are we going to measure their progress and quality?
A procurement strategy helps you organize suppliers, consultants, contractors, and requirements in a single place. Such a strategy usually requires –
- Creating the ‘Terms of Reference’ – a document that specifies the work of the external contractor
- Sending the ‘Request for Proposal’ to the procurement bidders, which also includes the Terms of Reference
- Creating the financial documentation, which includes the invoices and bills
Here’s an example of a procurement plan –
| Requirement | Terms of Reference | Invitation to Tender | Advertised (date) | Awarded (date) | Completed (date) |
| Logo design | logo_tor.pdf | email to designers | 1/7/2019 | 5/7/2019 | 31/7/2019 |
| App development | test_tor.pdf | developer_rfp.pdf | 5/8/2019 | 10/8/2019 | N/A |
6. Risk Register
Even the most systematically planned projects sometimes fall prey to unforeseen issues. So, there isn’t a way where you can stay far away from risks, but you can always minimize its impact.
Risk register involves assessing potential risks to determine the likelihood and impact of risks and then developing strategies to mitigate or avoid these risks, ensuring the project stays on track. It’s about creating backup plans and a proactive approach to ensure your project can handle unforeseen challenges without derailing its progress.
Here’s an example of a risk register table –
| Risk | Probability level (A-E) | Impact level (A-E) | Priority (A-E) | Triggers | Response Plan |
| The same app launched in the meantime | C | B | B | Lower app demand, decreased public interest, lower app price | Upgrading the app to offer a couple of additional features |
| Software bugs | D | A | A | Poor user experience | Re-development of problematic features |
Already procrastinating that you need to create all those tables for risk management?
Well, don’t worry because if you are considering investing in project management software, there won’t be any need to create such tables. Why don’t you try it yourself?
Read More: 9 Emerging Project Management Trends in 2024
7. Stakeholder Engagement
Stakeholder buy-in is crucial. Engaging stakeholders involves identifying them, understanding their expectations, and involving them in the project through regular communication and consultation. Let me give you an example.
In a community development project, engaging stakeholders (local government, residents, and businesses) would involve regular communication, addressing concerns, and adjusting project plans based on feedback to ensure community support.
One of the best things I’ve seen many project managers do is invite stakeholders to the project management platform. It boosts transparency and trust as stakeholders can check project progress, communicate with the team when needed, and oversee everything.
For example, in ProProfs Project, you can add clients and stakeholders as ‘guests’ and even choose what they can view in the project.
(Image source: ProProfs Project)
8. Communication Management
A communication plan stresses how information will be shared among project stakeholders. It specifies what will be communicated, when, how, and by whom. Effective communication is critical for ensuring everyone is aligned and informed throughout the project.
So, what you need to do is establish clear communication channels – regular meetings, status reports, and a central repository for project documents. For large, multi-departmental projects, regular status meetings, detailed reports to stakeholders, and the use of collaborative software are a must.
Also, talking about software, make sure your project management system lets you –
- Set up teams for different projects
- Share files with the team
- Add task comments for easy collaboration
- Track time to allocate hours for individual tasks
- Send automated reminders and task notifications to assigned team members
- Tag people working on the project using @mentions
(Image source: ProProfs Project)
This will ensure you don’t need to invest or switch to any second software to communicate with the team.
Read More: 15+ Team Communication Tools for Fast-Growing Organizations
9. Quality Management
Delivering a subpar product isn’t an option. Quality standards ensure the project’s deliverables meet the required specifications and satisfy stakeholder expectations for Elements of Project Management.
This element involves setting quality criteria, implementing quality assurance processes, and conducting quality control measures to maintain the desired level of quality.
For example, in a healthcare project aimed at improving patient care by implementing a small practice emr, quality management would focus on establishing standards based on best practices, conducting regular audits, and introducing a culture of continuous improvement among staff.
Want another example? Here’s what quality standards for a mobile application development project should be like –
- The app should be installed in less than 20 seconds.
- It should load in less than 5 seconds.
- The UI should cater to the target audience and their level of tech-savviness.
- The app should be able to perform various functions at the same time.
- The UX should provide a sleek experience with no bugs or delays.
Read More: Project Quality Management 101: Benefits, Elements & Tools
What Is the Most Important Part of a Project Plan?
Well-defined and robust plans that include diverse Elements of Project Management are meant to succeed. While it is easy to assume that time and financial factors are the key elements that need to be taken the most care of, it’s not really the reality.
In fact, there are several other elements that contribute equally to the success of a project, such as –
- Scope and success criteria definition
- The identification of potential risks and the best ways of dealing with them
- The specification of deliverables, as well as quality standards determination
- Project team organization and efficient communication
- Stakeholders’ interests and their power over your project results, etc.
On top of these, investing in a reliable project management system is also crucial. One of those tools that has worked well for me is ProProfs Project. It is one of those software solutions that present a wide range of features – resource management, risk mitigation, scope management, team communication and collaboration, etc.
But one thing you should remember before choosing any software is to test it first. Look for free trials or plans offered by software vendors. You can take ProProfs’ freemium plan as a reference, which I think is great for startups or SMBs who are first-time users. Try it today!
Learn More About Project Management Elements & Components
Why is project planning essential?
Project planning acts as a roadmap, ensuring everyone’s aligned, tasks are prioritized, and roadblocks are identified before they cause problems. It keeps projects on track, avoids delays, and keeps stakeholders happy.
Here are some of the key benefits of project planning:
- Increased Efficiency: A clear plan avoids wasted time and effort.
- Improved Communication: Everyone knows their roles and responsibilities.
- Enhanced Risk Management planning: Proactive identification and mitigation of potential issues.
- Better Resource Allocation: Resources are assigned effectively to meet project needs.
- Boosted Team Morale: A clear roadmap keeps teams motivated and focused.
What is ‘scope’ in project management?
In project management, ‘scope’ refers to the detailed set of deliverables or features of a project. It defines what will and will not be included in the project’s end result in Elements of Project Management.
How do I determine a project timeline?
To determine the timeline of a project, here’s what you need to do –
- List all tasks and their dependencies (related tasks).
- Estimate each task’s duration realistically.
- Sequence tasks based on dependencies and criticality.
- Use scheduling tools (Gantt charts) to visualize the timeline and track progress.
- Be flexible and refine the schedule as needed.
Read More: What Is Project Quality Management: A Project Manager’s Guide in 2024
What is a project budget?
A project budget is an estimation of the financial resources required for the completion of a project. It includes a detailed estimate of all project costs, including labor, materials, and potential contingencies. Tracking expenses helps you stay within budget and avoid financial surprises.
How is risk management applied in project management?
Applying risk management in project management is simple. This is what you need to do –
- Identify potential risks that could derail your project
- Develop contingency plans to mitigate those risks (how you’ll address them if they occur)
- Use a risk management tools solution
- This proactive approach ensures you’re prepared for unforeseen challenges and can react quickly
Who are project stakeholders?
Project stakeholders are individuals or organizations that have an interest in or are affected by the project’s outcome. This includes clients, sponsors, team members, and even end-users.
FREE. All Features. FOREVER!
Try our Forever FREE account with all premium features!